參考網站:
OpenVPN System Based On User/Password Authentication with mysql & Day Control (shell script)- Debian ~ Mr.TUM’s Blog
參考網站中,OpenVPN 和 MySQL 分別屬於不同主機,在這裡改用同一主機。
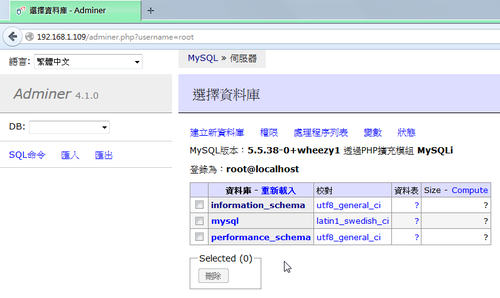
1. 安裝 MySQL Server
# apt-get install mariadb-server[@more@]2. 設定 root 密碼及一些安全性上的設定
# /usr/bin/mysql_secure_installation
還未設定 root 密碼,所以直接按 Enter 鍵
Enter current password for root (enter for none):
OK, successfully used password, moving on…
Setting the root password ensures that nobody can log into the MariaDB
root user without the proper authorisation.
設定 MySQL root 密碼
Set root password? [Y/n]
New password:
Re-enter new password:
Password updated successfully!
Reloading privilege tables..
… Success!
By default, a MariaDB installation has an anonymous user, allowing anyone
to log into MariaDB without having to have a user account created for
them. This is intended only for testing, and to make the installation
go a bit smoother. You should remove them before moving into a
production environment.
移除匿名使用者
Remove anonymous users? [Y/n]
… Success!
Normally, root should only be allowed to connect from ‘localhost’. This
ensures that someone cannot guess at the root password from the network.
取消 root 可以遠端登入
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n]
… Success!
By default, MariaDB comes with a database named ‘test’ that anyone can
access. This is also intended only for testing, and should be removed
before moving into a production environment.
移除 測試的資料庫
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n]
– Dropping test database…
… Success!
– Removing privileges on test database…
… Success!
Reloading the privilege tables will ensure that all changes made so far
will take effect immediately.
重新載入資料表權限
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n]
… Success!
Cleaning up…
3. 建立 openvpn 資料庫,並建立一個使用者及設定密碼來進行管理
# /usr/bin/mysql -u root -p
MariaDB [(none)]> CREATE DATABASE openvpn;
MariaDB [(none)]> GRANT ALL ON openvpn.* TO ‘pi’@”%” IDENTIFIED BY ‘123456’;
MariaDB [(none)]> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
MariaDB [(none)]> exit;
4. 改用 pi 使用者來建立 openvpn 相關資料庫設定
# /usr/bin/mysql -u pi -p
5. 開啟 openvpn 資料庫
MariaDB [(none)]> USE openvpn;
6. 建立 user 資料表
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `user` (
`user_id` varchar(32) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
`user_pass` varchar(32) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci NOT NULL DEFAULT ‘1234’,
`user_mail` varchar(64) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci DEFAULT NULL,
`user_phone` varchar(16) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci DEFAULT NULL,
`user_online` tinyint(1) NOT NULL DEFAULT ‘0’,
`user_enable` tinyint(1) NOT NULL DEFAULT ‘1’,
`user_start_date` date NOT NULL,
`user_end_date` date NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`user_id`),
KEY `user_pass` (`user_pass`)
) ENGINE=MyISAM DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_unicode_ci;
7. 建立 log 資料表
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `log` (
`log_id` int(10) unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`user_id` varchar(32) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci NOT NULL,
`log_trusted_ip` varchar(32) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci DEFAULT NULL,
`log_trusted_port` varchar(16) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci DEFAULT NULL,
`log_remote_ip` varchar(32) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci DEFAULT NULL,
`log_remote_port` varchar(16) COLLATE utf8_unicode_ci DEFAULT NULL,
`log_start_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
`log_end_time` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT ‘0000-00-00 00:00:00’,
`log_received` float NOT NULL DEFAULT ‘0’,
`log_send` float NOT NULL DEFAULT ‘0’,
PRIMARY KEY (`log_id`),
KEY `user_id` (`user_id`)
) ENGINE=MyISAM DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_unicode_ci;
8. 建立使用者資料
INSERT INTO `user` (
`user_id`, `user_pass`, `user_mail`, `user_phone`,
`user_online`, `user_enable`, `user_start_date`, `user_end_date`
)
VALUES (
‘test’, ‘123456’, ‘test@test.com’,
‘+66815447514’, 0, 1, ‘2012-01-01’, ‘0000-00-00’
);
9. 顯示資料庫中的資料表
MariaDB [openvpn]> show tables;
+————————–+
| Tables_in_openvpn |
+—————————+
| log |
| user |
+—————————-+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
10. 列出 user 資料表中的使用者資料
MariaDB [openvpn]> select user_id,user_pass from user;
+———-+—————-+
| user_id | user_pass |
+———-+—————–+
| test | 123456 |
+———-+—————–+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
11. 退出資料庫
MariaDB [openvpn]> exit;
12 . 建立 Script 檔目錄 /etc/openvpn/script
# mkdir /etc/openvpn/script
13. 建立 /etc/openvpn/script/config.sh
# cat etc/openvpn/script/config.sh
#!/bin/bash
##Dababase Server
HOST=’127.0.0.1′
#Default port = 3306
PORT=’3306′
#Username
USER=’pi’
#Password
PASS=’123456′
#database name
DB=’openvpn’
14. 建立 /etc/openvpn/script/test_connect_db.sh
# cat /etc/openvpn/script/test_connect_db.sh
#!/bin/bash
. /etc/openvpn/script/config.sh
##Test Authentication
username=$1
password=$2
user_id=$(mysql -h$HOST -P$PORT -u$USER -p$PASS $DB -sN -e “select user_id from user where user_id = ‘$username’ AND user_pass = ‘$password’ AND user_enable=1 AND user_start_date != user_end_date AND TO_DAYS(now()) >= TO_DAYS(user_start_date) AND (TO_DAYS(now()) <= TO_DAYS(user_end_date) OR user_end_date=’0000-00-00′)”)
##Check user
[ “$user_id” != ” ] && [ “$user_id” = “$username” ] && echo “user : $username” && echo ‘authentication ok.’ && exit 0 || echo ‘authentication failed.’; exit 1
15. 建立 /etc/openvpn/script/login.sh
# cat /etc/openvpn/script/login.sh
#!/bin/bash
. /etc/openvpn/script/config.sh
##Authentication
user_id=$(mysql -h$HOST -P$PORT -u$USER -p$PASS $DB -sN -e “select user_id from user where user_id = ‘$username’ AND user_pass = ‘$password’ AND user_enable=1 AND user_start_date != user_end_date AND TO_DAYS(now()) >= TO_DAYS(user_start_date) AND (TO_DAYS(now()) <= TO_DAYS(user_end_date) OR user_end_date=’0000-00-00′)”)
##Check user
[ “$user_id” != ” ] && [ “$user_id” = “$username” ] && echo “user : $username” && echo ‘authentication ok.’ && exit 0 || echo ‘authentication failed.’; exit 1
16. 建立 /etc/openvpn/script/connect.sh
# cat /etc/openvpn/script/connect.sh
#!/bin/bash
. /etc/openvpn/script/config.sh
##insert data connection to table log
mysql -h$HOST -P$PORT -u$USER -p$PASS $DB -e “INSERT INTO log (log_id,user_id,log_trusted_ip,log_trusted_port,log_remote_ip,log_remote_port,log_start_time,log_end_time,log_received,log_send) VALUES(NULL,’$common_name’,’$trusted_ip’,’$trusted_port’,’$ifconfig_pool_remote_ip’,’$remote_port_1′,now(),’0000-00-00 00:00:00′,’$bytes_received’,’$bytes_sent’)”
##set status online to user connected
mysql -h$HOST -P$PORT -u$USER -p$PASS $DB -e “UPDATE user SET user_online=1 WHERE user_id=’$common_name'”
17. 建立 /etc/openvpn/script/disconnect.sh
# cat /etc/openvpn/script/disconnect.sh
#!/bin/bash
. /etc/openvpn/script/config.sh
##set status offline to user disconnected
mysql -h$HOST -P$PORT -u$USER -p$PASS $DB -e “UPDATE user SET user_online=0 WHERE user_id=’$common_name'”
##insert data disconnected to table log
mysql -h$HOST -P$PORT -u$USER -p$PASS $DB -e “UPDATE log SET log_end_time=now(),log_received=’$bytes_received’,log_send=’$bytes_sent’ WHERE log_trusted_ip=’$trusted_ip’ AND log_trusted_port=’$trusted_port’ AND user_id=’$common_name’ AND log_end_time=’0000-00-00 00:00:00′”
18. 更改 Script 檔案權限
# chmod 755 /etc/openvpn/script/*.sh
19. 修改 /etc/openvpn/server.conf 設定檔
# vim /etc/openvpn/server.conf
加入以下設定
username-as-common-name
client-cert-not-required
auth-user-pass-verify /etc/openvpn/script/login.sh via-env
# 設定使用者登入及登出時要做的動作
##script connect-disconnect
script-security 3 system
client-connect /etc/openvpn/script/connect.sh
client-disconnect /etc/openvpn/script/disconnect.sh
20. 測試 MariaDB SQL Server 可否正常連線(帳號/密碼:test / 123456)
# /etc/openvpn/script/test_connect_db.sh test 123456
user : test
authentication ok.
如果是上面的訊息,則是連線成功!
21. 設定 OpenVPN Client 端 *.ovpn
加入以下設定
auth-user-pass
reneg-sec 0
22. 重新啟動 OpenVPN Server
# systemctl restart openvpn@server.service
23. 列出使用者的登入資料
MariaDB [openvpn]> select user_id,log_trusted_ip,log_remote_ip,log_start_time,log_end_time from log;
+———-+——————–+———————+——————————+—————————–+
| user_id | log_trusted_ip | log_remote_ip | log_start_time | log_end_time |
+———-+——————–+———————+——————————+——————————+
| test | 1.162.15.9 | 10.8.0.6 | 2016-12-29 09:27:32 | 2016-12-29 10:27:36 |
+———-+——————–+———————+——————————+——————————+